Introduction
The Communication Infrastructure
The SafeTRIP Middleware
The On-Board Unit (OBU)
Case Studies
Business Models for SafeTRIP Platform
Service Definition
The aim of this section is to clarify some concepts related to the service oriented architecture on which the Service Enabling Platform is based. Part of the following is based on documents copyrighted by OASIS® (Organization for the Advancement of Structured Information Standards) which has given permission for their use.
In particular, this section will provide the Definition of Service, Service Ecosystem, Service Oriented Architecture, SafeTRIP Service Architecture, Service Centres and Service Model.
Definition of Service
The meaning of the word service is: “The performance of work (a function) by one for another”. Generally speaking the concept of SERVICE includes:
- the capability to perform work for another
- the specification of the work offered on behalf of another
- the offer to perform work for another.
The SERVICE concept is associated to a set of functions which work together for a specific purpose (e.g. chat service, video service or voice service), which may or may not be destined for the end users.
On the other hand, a SERVICE APPLICATION is a PACKAGE OF SERVICES ready to be used by the end-users.
One SERVICE APPLICATION could be made with a single service, for instance the telephony with the voice service, or be made with a set of services, for instance the Videoconference with the voice, video, chat, file transfer services.
An APPLICATION can invoke one or more services.
The main distinction is that when speaking about a SERVICE - there is always a PROVIDER and a CONSUMER (customer). Whereas for an "application-alone” case these characteristics are not mandatory.
Service Ecosystem
In order to understand the interactions that occur in the service provisioning process it is important to clarify the meaning of some core words:
- Actor: an entity, human, non-human or organization of entities, that is capable of action
- Stakeholder: an individual entity, human or non-human, or organization of entities that has an interest in the state of the ecosystem
- Participant: a stakeholder that is an actor
- Non-Participant Stakeholder: any stakeholder who is not an actor in the ecosystem
- Delegate: an actor that is acting on behalf of a participant
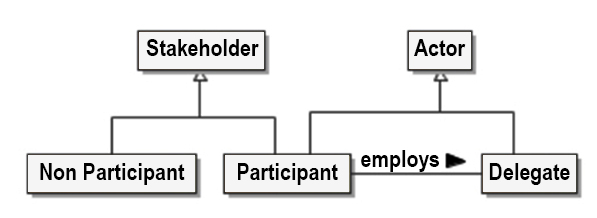
Figure 9: Service Actors
- Service Provider: a participant that offers a service that enables some capability to be used by other participants
- Service Consumer: a participant that interacts with a service in order to realize the real world effect produced by a capability to address a consumer need
- Service Mediator: a participant that facilitates the offering or use of services in some way
- Need: a measurable requirement that a service participant is actively seeking to satisfy
- Capability: an ability to achieve a real world effect
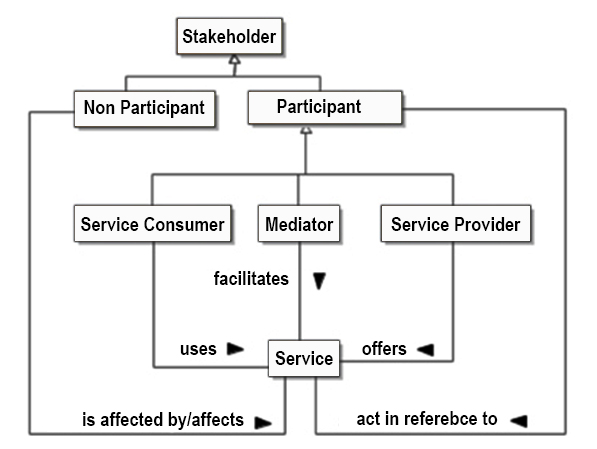
Service Oriented Architecture
A service-oriented architecture is a collection of services that communicate with each other. This communication can involve either simple data passing or it could involve two or more services coordinating an activity. Some means of connecting services to each other is needed.
SafeTRIP Service Architecture
The service architecture of SafeTRIP is organized into two main layers:
- Enabling Services
- End User Services - Applications
Enabling services are not oriented to end users and are provided by the Service Enabling Platform (SEP). The service consumers for this category of services are end-user devices and the SafeTRIP network.
Enabling services are: Authentication, authorization, accounting, quality of service control, vertical handover control.
The service providers for end-user services and applications are stakeholders internal or external to the SafeTRIP network; service consumers are SafeTRIP end users.
End user services and applications are: Value added services, including security, localization, emergency call, e-alert, communication, etc.
End-user services cannot be provided without enabling services that act as mediators between providers and consumers.
Service Centres
The Service Centres shall include two categories of actors:
- Value Added Service Provider (VASP)
- Existing Service Providers (ESP)
Value Added Service Provider (VASPs) are the actors that actually provide value added services. In this group there are:
- Data broadcasters
- Content providers
- Content aggregators
Existing Service Providers (ESP) are the actors of the system which users have subscribed to. ESPs may be Telecommunications operators, Road operators, Insurance companies, Public institutions etc.
ESPs have an agreement with the SafeTRIP platform to provide their users with value added services using the SafeTRIP network. This means that contractual details (e.g. contractual data rates, number of accesses per day to a given content, etc.) are kept by ESPs and provided to the Service Enabling Platform on request.
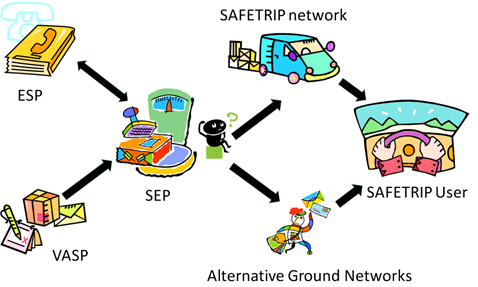
Figure 11: SafeTRIP Service EcoSystem
It is possible for the ESP and VASP to be the same actor: this is the case with a company that provides services only to its own subscribers. ITSP (Internet Telephony Service Provider) is an example of this as it provides VoIP services to subscribed users.
Service Model
The following diagram illustrates the service model adopted in SafeTRIP.
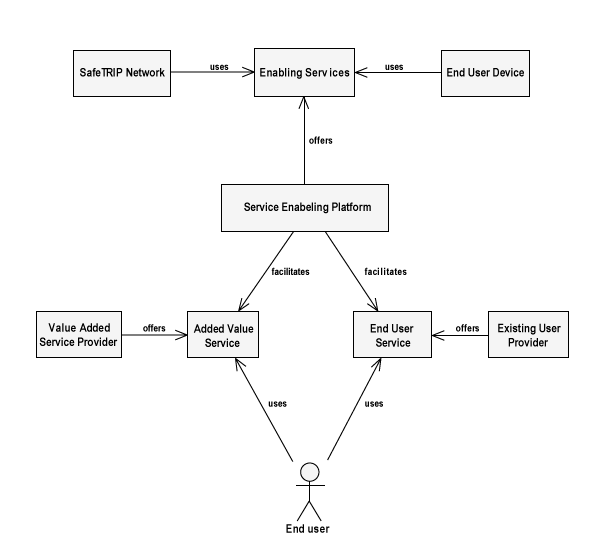
Figure 12: SafeTRIP Service Roles
The Service Enabling Platform offers Enabling Services that are used by the SafeTRIP Network and End User Devices. The SEP also facilitates VASPs and ESPs in the provisioning of their services.



